Dhealthwellness.com – A physician can perform an ultrasound to confirm a diagnosis of disease hemangiomas. Ultrasound uses sound wave technology to show blood flow through the affected area. A physician may also use an MRI to determine the location and size of the hemangioma and its relationship with nearby structures. Medications may be prescribed to slow the growth of the hemangioma and shrink it. A physician may recommend laser therapy or surgery if the hemangioma is growing larger than normal.
Types of Treatment for Hemangiomas
Treatment for hemangiomas can include observation, laser therapy, and drug therapies. Surgery may be required for larger lesions. Combinations of these treatments may be prescribed depending on the type of hemangioma. Drug treatments can be prescribed by a doctor, but often the best results come from a combination of treatments. For small lesions, corticosteroids may be applied. Some doctors prescribe oral corticosteroids.
The growth of hemangiomas in children can vary. The first year of life is the fastest, followed by a period when the tumor shrinks. During this period, the majority of hemangiomas will disappear on their own, although some may pose a threat to essential functions. If left untreated, hemangiomas can linger for years, causing emotional and physical challenges. However, with early detection and treatment, most hemangiomas will shrink.
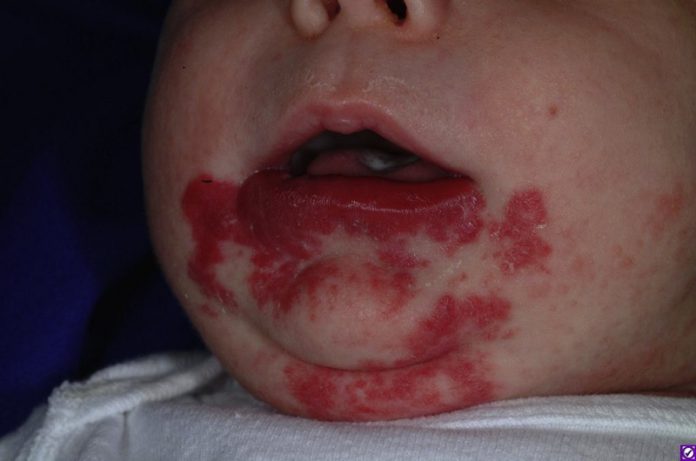
Children with hemangioma may exhibit other signs of vascular malformations, such as bleeding and infection. While hemangiomas typically appear on the skin, they are not inherited. However, some families may have suffered from a family member with a similar hemangioma. In addition to the skin, hemangiomas may occur in other parts of the body. A specialized clinic specializes in the treatment of hemangiomas.
Non-cancerous Blood Vessel Growth
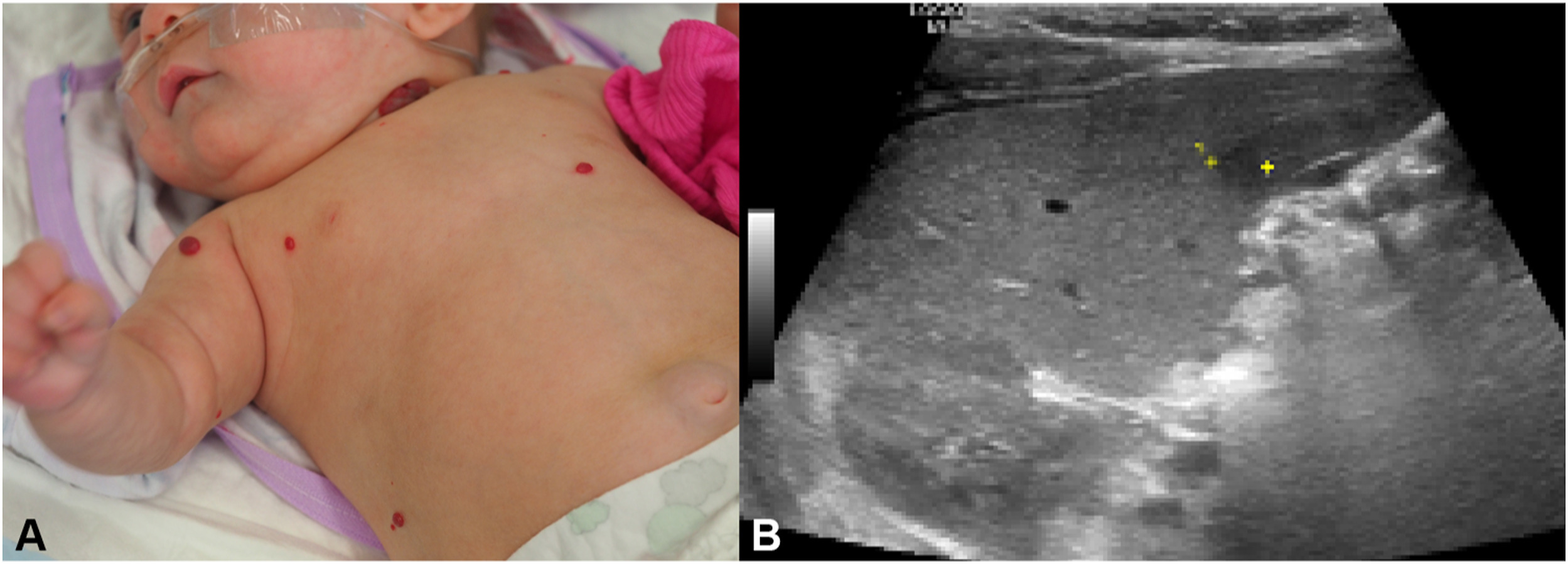
Hemangiomas in children are noncancerous blood vessel growths that generally subside on their own without treatment. Some hemangiomas may open and bleed, or may be painful or disfiguring. If they become large, they may require surgical removal. If they continue to grow, there may be other abnormalities in the affected area. The treatment for hemangioma depends on its size and location. If it is symptomatic, treatment may be unnecessary.
Hemangiomas in children may appear at birth or in early childhood. They generally begin as small, flat red marks on the skin and gradually grow. They may spread to other parts of the body and affect the child’s breathing. The most common locations for hemangiomas in infants are the face, chest, and back. Although hemangiomas rarely require treatment, they may need periodic checkups. They may recur after they have been removed.\
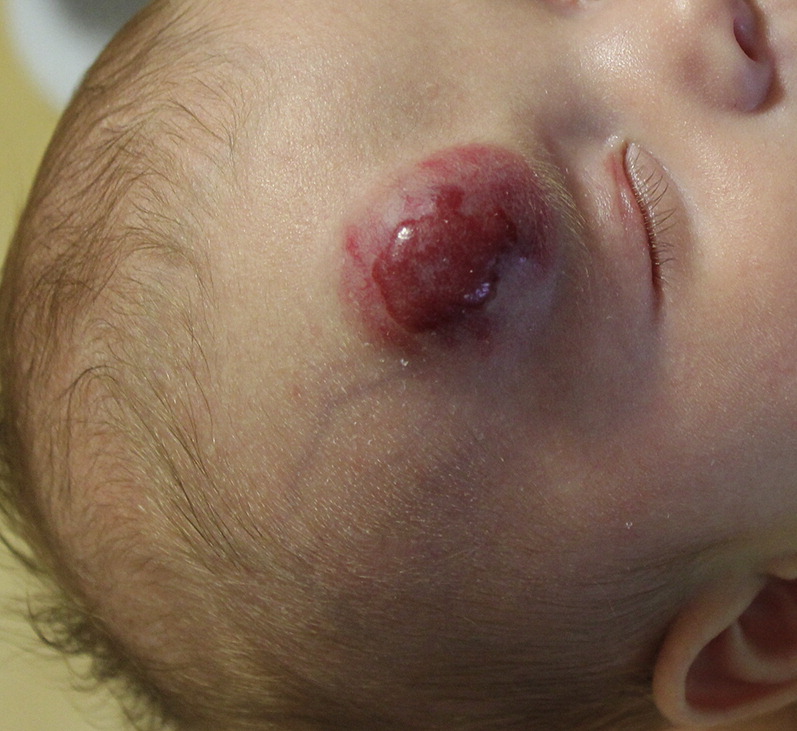
In the majority of cases, the hepatic hemangioma is benign, and if it’s under 10 cm, it is unlikely to cause any symptoms. However, those under 10 cm usually require no treatment. A posthumous case report of a male child with a medium-sized hemangioma describes the difficulties of treating a child with a complicated condition in a resource-limited setting.
Genetics May Play a Role in Liver Hemangioma Development
Liver hemangioma, also known as hepatic hemangioma, is a cluster of blood vessels that are noncancerous. It usually does not cause any symptoms and does not spread to other organs. It affects between one and five percent of U.S. adults. Most people with hemangiomas are men, but women are three times more likely to develop the disease. Research indicates that genetics may play a role in the development of liver hemangiomas.
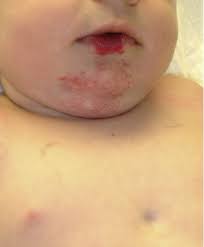 As the disease progresses, arteries may become increasingly narrow. Lack of blood flow to the brain can result in a stroke in affected individuals or children. Initial symptoms may include seizures and loss of feeling in one side of the body. As blood vessel problems progress, they can become life-threatening and cause brain damage. If not diagnosed in time, it can lead to a life-threatening situation. Hemangiomas are often difficult to detect, but treatment is possible.
As the disease progresses, arteries may become increasingly narrow. Lack of blood flow to the brain can result in a stroke in affected individuals or children. Initial symptoms may include seizures and loss of feeling in one side of the body. As blood vessel problems progress, they can become life-threatening and cause brain damage. If not diagnosed in time, it can lead to a life-threatening situation. Hemangiomas are often difficult to detect, but treatment is possible.
Reference: