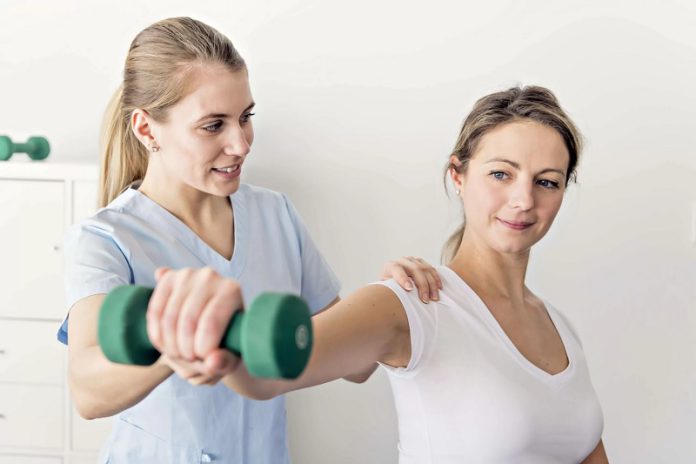
Dhealthwellness.com – Shoulder Physical Therapy can be a valuable tool for recovering from a shoulder injury. The goal of shoulder physical therapy is to help patients regain mobility and strength. Patients may be prescribed home exercises to help them continue their recovery after treatment. Physical therapists will also recommend home activities to help patients maintain mobility. Treatment plans may include a home exercise routine and exercises to strengthen the muscles of the shoulder. Following a treatment plan, patients can begin normal activities and avoid re-injuring the shoulder.
Determining the Best Treatment by a Physical Therapist
During therapy sessions, physical therapists will perform various range-of-motion tests to determine joint mobility and strength. They will also use modalities to relax the muscles. In addition to this, they may prescribe a home-exercise routine to help patients improve their flexibility and avoid shoulder pain in the future. A physical therapist will be able to determine the best course of treatment based on the results of these tests.
Shoulder injuries can disrupt the delicate balance of the joint, causing pain, loss of motion, and decreased strength. They can also interfere with everyday activities, such as lifting heavy objects and household items. Shoulder injuries are often the result of overuse or trauma. The surrounding soft tissues, muscles, and tendons are often injured in sports or other activities. In some cases, a shoulder joint replacement may be necessary, which can result in significant pain and limited functionality.

Shoulder Physical Therapy uses simple equipment such as a wand, rope and pulley, elastic bands, and tubes. Many people use a broom as a wand. Some exercises are best performed while lying on one’s back. Proper elbow support is essential during some exercises, but a fluffy pillow should not be used instead of a stack of blankets. A limited role is also reserved for free weights, which may be used selectively.
Special Rehabilitation can Help Get Back to Activities
Once the shoulder is stabilized, physical therapists can develop a specialized rehabilitation program that will help you return to activities. Physical therapists will work closely with a patient to develop a customized rehabilitation program that will help them return to normal activities as soon as possible. Full recovery after shoulder surgery can take six to eight weeks. The goal of physical therapy is to improve range of motion and strength. The physical therapist will work with you to create a tailored treatment plan based on your needs and goals.
Shoulder aches are often caused by rotator cuff impingement, a condition that limits shoulder mobility. Physical therapists can help restore mobility and comfort by strengthening muscles that support the rotator cuff. Depending on your level of injury, your physical therapist may also recommend a home exercise program to help you get back to normal activities. You can even seek surgical intervention after physical therapy. If this does not work, your doctor will prescribe a strengthening program.
Exercises are very important to the recovery process after shoulder surgery. Physical therapists help patients regain range of motion by teaching them how to move correctly in different positions. Exercises that improve shoulder mobility include isometric contractions, resistance band exercises, and free weights. It is important to know how to perform functional exercises so you can prevent further injury. Physical therapists can also use functional training to teach you how to lift a glass into a cupboard.
Strengthening the Muscles that Support the Joints
Shoulder fractures can cause instability in the joint. Traumatic injuries involve the humerus, scapula, and clavicle. A shoulder fracture may occur as a result of direct contact with an object or from overuse. Depending on the severity, you may need surgery to repair the joint. Shoulder physical therapy will help strengthen the muscles that support the joint. If you’ve been injured by a traumatic accident, seek treatment as soon as possible.
While a physical therapist may not be able to identify a frozen shoulder during stage one, symptoms will be apparent in about 12 months. The patient may feel pain on movement but their range of motion is rapidly improved. The patient may lose motion in the external rotation of the shoulder, while reaching behind the back may be affected. Physical therapists will recommend resting frequently between physical therapy sessions in order to minimize the formation of scar tissue in the shoulder.

After a thorough medical history, the physical therapist will examine the patient’s shoulder. She will examine the various shoulder measures, including MRI, to determine whether a labral tear is the cause of the pain. She will also ask the patient to demonstrate positions or activities that cause pain and examine nearby areas. The physical therapist may also recommend tests for patients who may have a underlying condition that needs surgical repair. If the physical therapist suspects the shoulder pain is caused by a tear in the labrum, the therapist may refer the patient to an orthopedic surgeon.
Reference:
