Dhealthwellness.com – If you have had a sports injury, you may have heard of elastic therapeutic tape. Also known as kinesiology tape, this bandage is made of cotton with an acrylic adhesive. It is allegedly effective in helping ease pain associated with various physical disorders and athletic injuries. But is it really effective? Let’s take a look. The benefits of elastic therapeutic tape are many and varied. Using it properly can help prevent or alleviate pain and discomfort, and it has many uses.
Identifying Factors Affecting Band Therapy Performance
Various tests have been conducted to determine the holding capacity of the therapeutic tape. The first test, called the stress relaxation test, involves measuring the change in length after 300 cycles. It analyzes the effect of different strain values on the holding capacity of the therapeutic tape. This test was conducted at room temperature under constant min-max load. This analysis allows researchers to identify the factors that can influence the holding capacity of the therapeutic tape. Further, the stress relaxation test is useful in identifying the factors that influence therapeutic tape performance.
As the athletic tape is becoming increasingly popular, it can help athletes and other professionals maintain optimal posture. It supports the muscles that control posture, eliminating movement dysfunctions and correcting postural faults. The use of elastic therapeutic tape is relatively new to the athletic training community, with only a small body of relevant research. However, the benefits are clear. Here are some of the benefits of elastic therapeutic tape. A: It supports a variety of sports. It can help athletes avoid a number of injury-related conditions. It can also help athletes with pain relief.
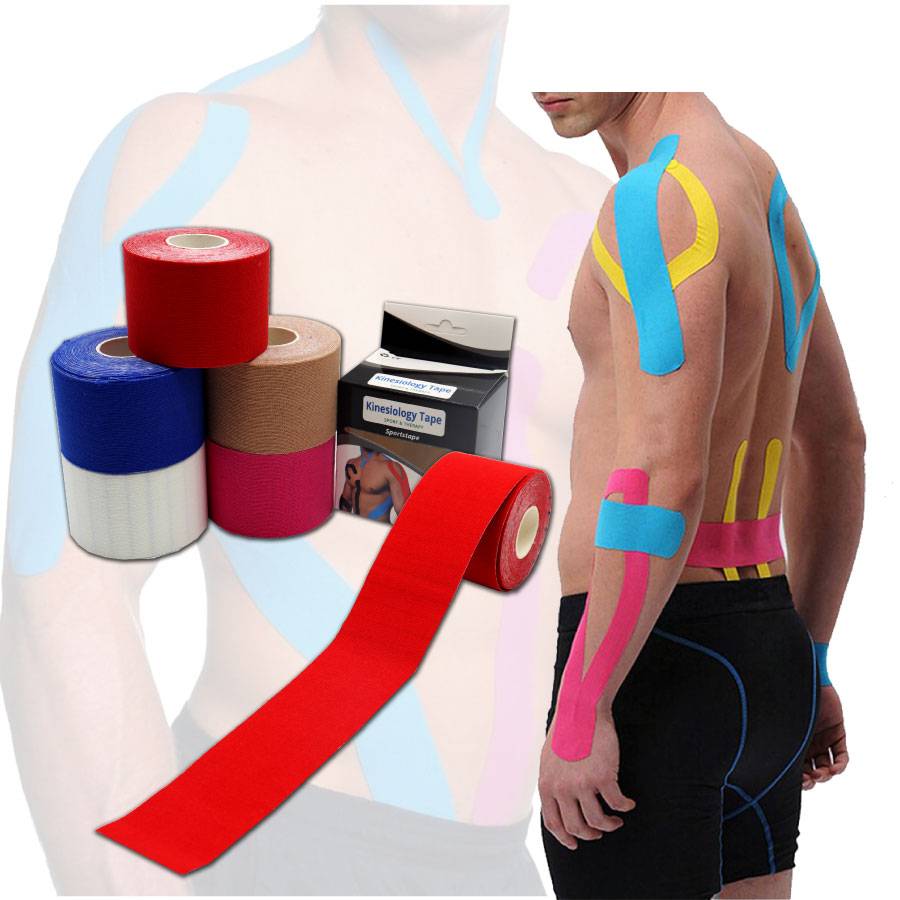
It doesn’t restrict range of motion, and it helps prevent and alleviate chronic muscle fatigue and cramps. But the best way to use elastic therapeutic tape is to see a qualified athletic trainer or doctor. This tape is effective in reducing inflammation and pain caused by sports injuries. And, it is effective in reducing inflammation, which makes it ideal for athletes. But it is important to note that not all research is devoted to the use of elastic therapeutic tape.
Helps Overcome Pain and Swelling
One of the benefits of elastic tape is that it can help with pain and swelling by lifting the skin. Using elastic tape on the body will also confuse the nerve endings that help transmit pain messages to the brain. This will help the brain recognize the pain as something outside the centralized area. In turn, this can help the muscles recover faster, reducing pain and discomfort overall. You can even use it for rehabilitation exercises and massage sessions.
Several brands of elastic therapeutic tape have been developed, and it’s important to understand the material properties of each type before choosing which one to use. Elastic therapeutic tapes can differ in their properties, and physical therapists and athletic trainers must understand their properties so that they can apply the tapes effectively. If they do, then the tape will be of high quality and will not cause discomfort. If you’re using elastic tape, make sure that it fits correctly and is easy to remove.
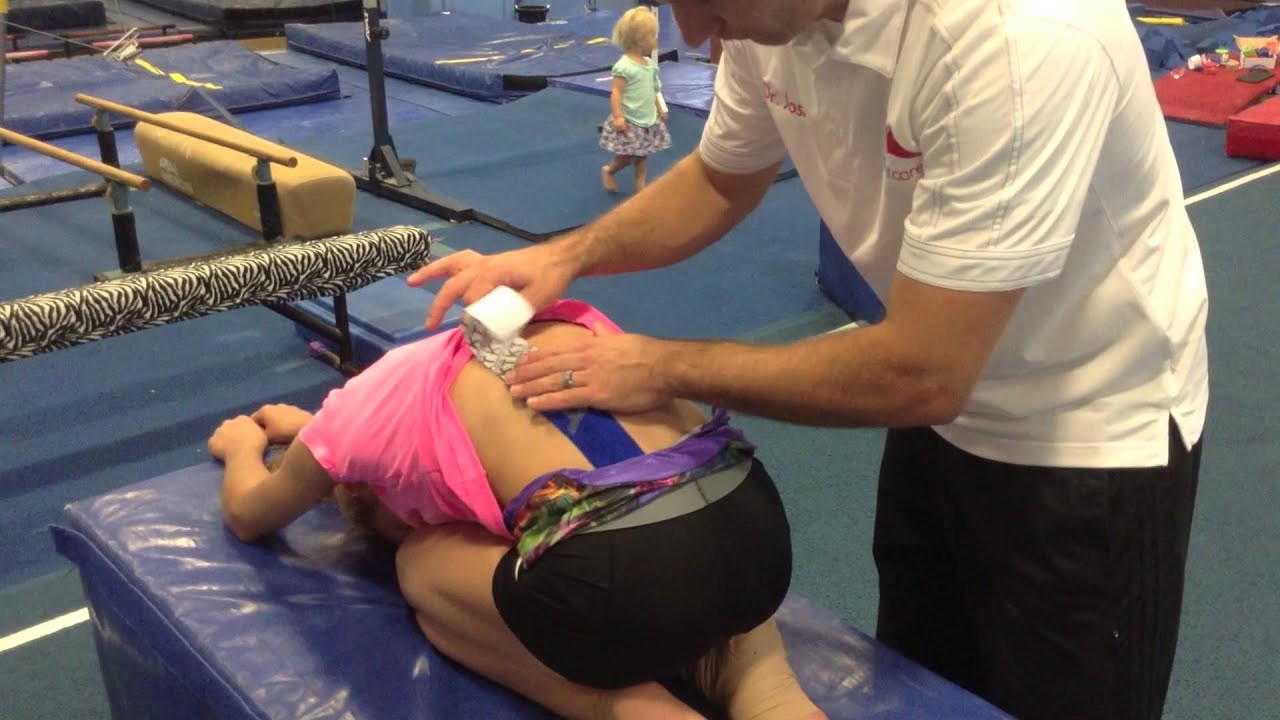

When applying tape to your body, your physical therapist will explain how to apply it. For the most part, tape must be applied with a gentle, even stretch. You can apply it in an X, Y, or I pattern. For specific problems, you can also apply decompression strips. You should practice applying the tape before you get a grip on it. The adhesive will usually take 20 minutes to fully adhere. However, after a few days, the tape will start to lose its grip.
Treating Soft Tissue Injury
Elastic therapeutic tape may help treat soft tissue injuries. Its use should be supervised by a physician, as it may cause risks to certain diseases. Because of the increase in fluid flow in the body, it should never be applied to sites of active malignancy, open wounds, or deep vein thromboses. Additionally, this tape can increase the risk of heart disease, congestive heart failure, and kidney problems.
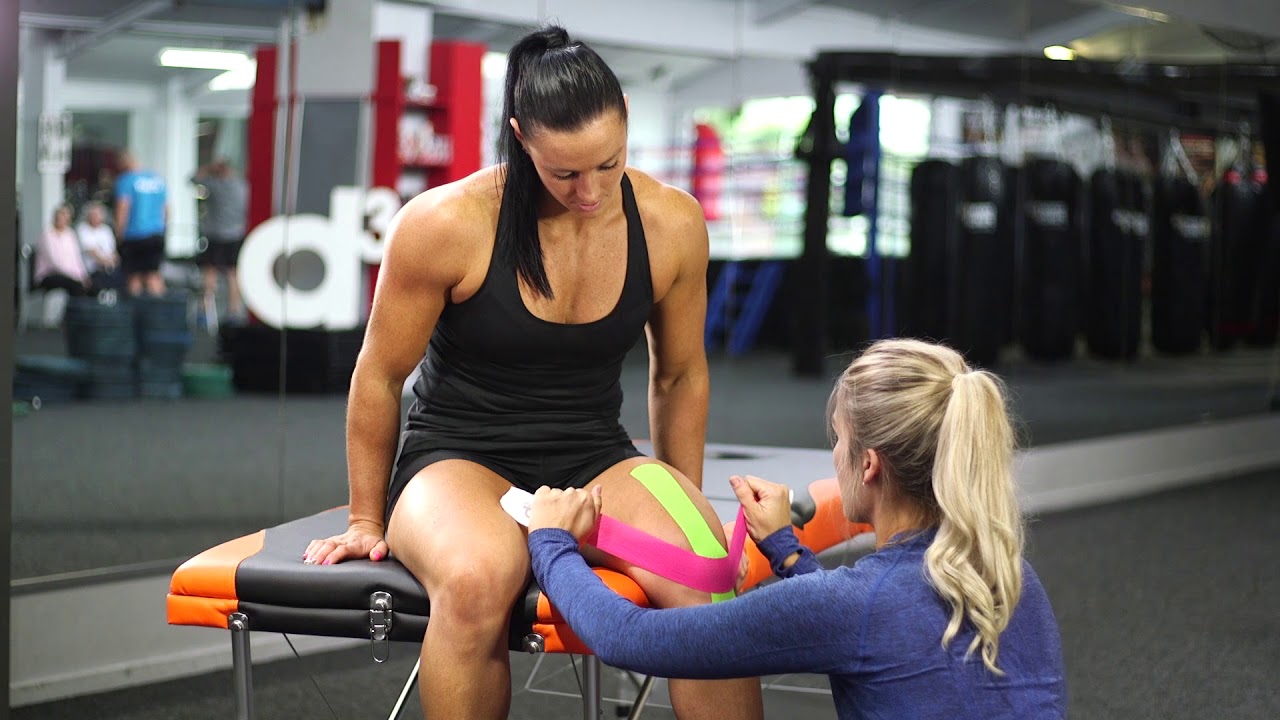

Although research is needed to determine the efficacy of ETT, the results suggest that it helps patients with residual weakness. A patient’s proprioception is aided by ETT and can improve efficiency in using muscles in rehabilitation. However, improper use can reduce efficacy. ETT may even be more effective in injured individuals than in healthy individuals. But the key to its effectiveness is a good training. Its benefits are obvious and should be worth a try.
Reference:
